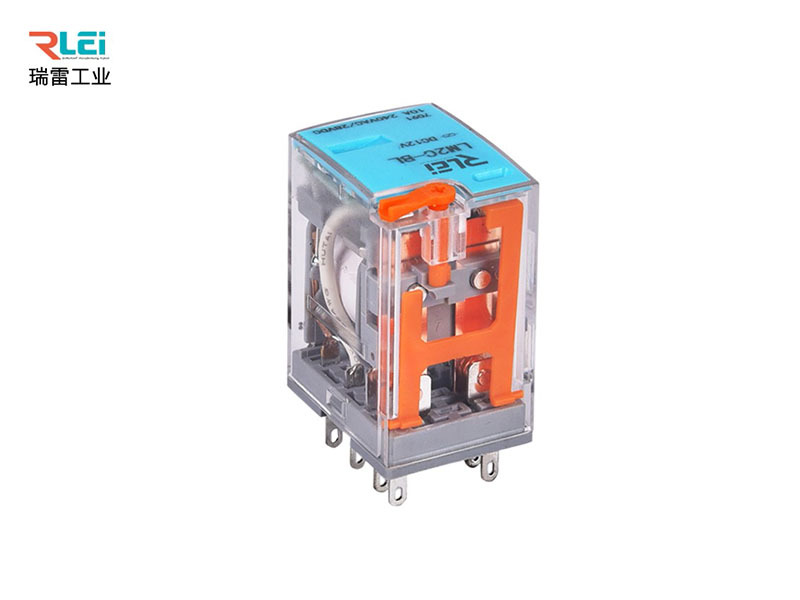
What is the function and principle of relay
2022-11-15
The use of relays in our home is very important, which can provide the most basic life guarantee for home life. However, we should also pay attention to the use of relays to avoid unnecessary troubles. Then what is the function and principle of relay, and the correct use of relay, do you understand? Now let's find out.
What does a relay do? What does a relay do
2022-11-15
Relay is a kind of electric control device, is when the change of the input quantity to meet the specified requirements, in the electrical output circuit to make the controlled quantity of a predetermined step change of an electrical appliance.
2022-11-15
The new relay refers to the electromagnetic relay developed and produced in order to meet the new special requirements and meet the use under special environmental conditions. Its main characteristics are small volume, light weight, vibration resistance, shock resistance, load range from low level load to 5A, 28V rated load, and the product has reliability index (failure rate level) requirements. The product adopts resistance fusion welding or laser fusion welding sealing air-tight sealing structure, mainly used in electronic control equipment signal transmission and weak current power switching.
2022-11-15
The impact of environment on the reliability of relays: the average time between failures of relays working in GB and SF is the highest, reaching 820000 hours, while in NU environment, it is only 60000hours.
2022-11-15
There are many types of relays, which can be divided into voltage relay, current relay, time relay, speed relay and pressure relay according to the input quantity, electromagnetic relay, induction relay, electric relay and electronic relay according to the working principle, and control relay and protection relay according to the purpose. According to the input quantity change form can be divided into whether there is a relay and measuring relay.
Symbolic representation of relays
2022-11-15
The relay coil is represented in the circuit by a long box symbol, and if the relay has two coils, two long boxes are drawn side by side. At the same time, mark the relay word symbol "J" in or beside the long box. There are two ways to represent the contacts of relays: one is to draw them directly on one side of the long box, which is more intuitive.
2022-11-15
Measure contact resistance: use the electric barrier of a multimeter to measure the resistance of normally closed contact and moving point, and the resistance value should be 0; The resistance of normally open contact and moving point is infinite. So you can tell that one is a normally closed contact and that one is a normally open contact.